Accounting Oveview, Importance, Types, Careers
Internal auditors review their companies’ accounting procedures and adherence to laws and regulations. They also assess financial records for potential areas of growth and increased efficiency. An entry-level role, accounting clerks conduct data entry tasks and verify calculations.
Accounting is important as it keeps a systematic record of the organization’s financial information. Up-to-date records help users compare current financial information to historical data. With full, consistent, and accurate records, it enables users to assess the performance of a company http://www.gkir.ru/mp3/albums/Z/ over a period of time. Accounting provides information for all these purposes through the maintenance of data, the analysis and interpretation of these data, and the preparation of various kinds of reports. It is also a well-paid profession, with the potential to earn a high salary.
Do you own a business?
Discover types of accounting, skills, salaries in different jobs, qualifications, and certifications, as well as the steps to getting started. According to the BLS, accountants in the U.S. earned a median annual income of $78,000 as of 2022. Depending on an accountant’s experience level, industry and location, they may make even more.
After President Biden signed a bill on Wednesday forcing Chinese company ByteDance to sell its ownership of TikTok, the United States moved one step closer to an internet without the short video app. The legislation opened the door to a possible ban of the social media platform if TikTok fails to find a U.S. government-approved http://zhenskaja-mechta.ru/real-money-slots-vs-online-slot-games buyer within a year. The Richmond Police Department, along with financial forensic analysts from the district attorney’s office, launched an investigation, which culminated in her arrest on April 19. This in turn funneled the money into her personal bank account, according to prosecutors.
Organizing financial transactions
The Canadian CPA designation is held by more than 200,000 members in Canada and around the world. The median annual pay for an accountant in the U.S. was $78,000 as of 2022, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Accountants may be held liable for paying uninsured losses to creditors and investors in the case of a misstatement, negligence, or fraud. Accountants must abide by the ethical standards and guiding principles of the region where they practice, such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Accountants work with companies, governments, and non-profits, or set up private practices.
The auditing industry for limited companies is regulated under the Companies Ordinance (Chapter 32, Laws of Hong Kong), and other ordinances such as the securities and futures ordinance, the listing rules, etc. CGA-Canada integrated with CPA Canada on October 1, 2014, completing the unification of Canada’s accounting profession at the national level. Excepting the Association of Certified Public Accountants, each of the above bodies admits members only after passing examinations and undergoing a period of relevant work experience.
Shareholders’ Equity Statement
For business owners without a bookkeeping or accounting background, the prospect can be overwhelming. The accounting profession covers a broad range of roles, including bookkeeping, tax planning, and audit. Accountants may become certified with designations, such as Certified Public Accountant https://www.e-lib.info/why-no-one-talks-about-anymore/ (CPA) in the U.S., Chartered Accountant (ACA) in the U.K., Chartered Professional Accountant (CPA) in Canada, and so on. The four largest accounting firms globally include Deloitte, KPMG, PwC, and EY. The role of an accountant is to responsibly report and interpret financial records.
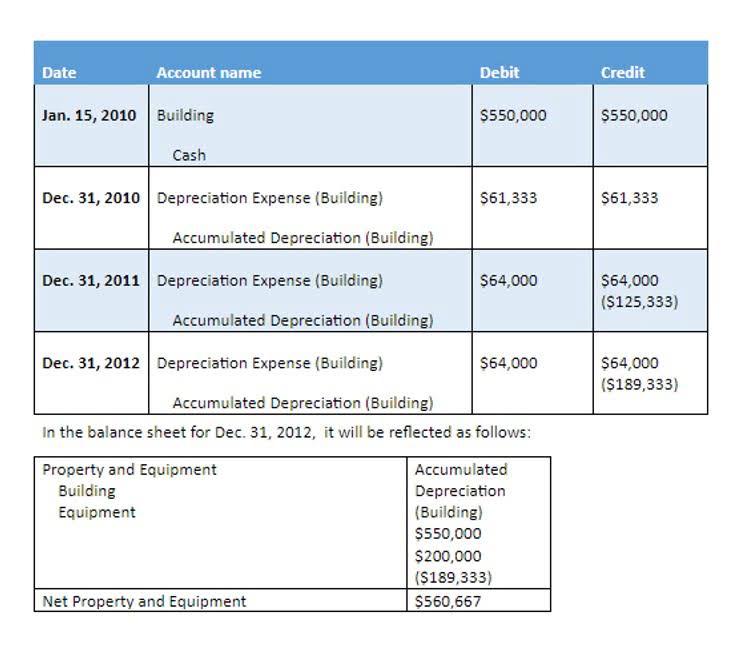
The financial statements include the income statement, the balance sheet, the cash flow statement, and the statement of retained earnings. The standardized reporting allows all stakeholders and shareholders to assess the performance of a business. This type of accounting involves an independent review of a company’s financial statements to ensure that they are accurate and in compliance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Auditors may also perform operational audits to assess an organization’s internal controls or compliance with standards such as Sarbanes-Oxley.
What is Accounting?
When the company earns the revenue next month, it clears the unearned revenue credit and records actual revenue, erasing the debt to cash. It’s also worth noting that while all CPAs are accountants, not all accountants are CPAs. The responsibilities of an accountant are numerous, and some of them may overlap with those of the bookkeeper. In a nutshell, the accountant understands and interprets a company’s financial health through the combination of his knowledge of numbers and accounting principles.
You must stay up-to-date on the latest changes to prepare your clients’ taxes properly. Additionally, tax accountants must be able to navigate the complex web of tax laws to find the best way to minimize their clients’ taxes and provide tax advice. Most accounting jobs will generally require at least a bachelor’s degree in accounting or a related field.