A Step-by-Step Guide on How to Calculate Overtime Pay

Commissions (whether based on a percentage of total sales or of sales in excess of a specified amount, or on some other formula) are payments for hours worked and must be included in the regular rate. Whether the commission earnings are computed daily, weekly, biweekly, semimonthly, monthly or at some other interval does not matter. That the commission is paid on a basis other than weekly and that payment is delayed for retained earnings balance sheet a time past the employee’s normal payday or pay period do not excuse the employer from including this payment in the employee’s regular rate.

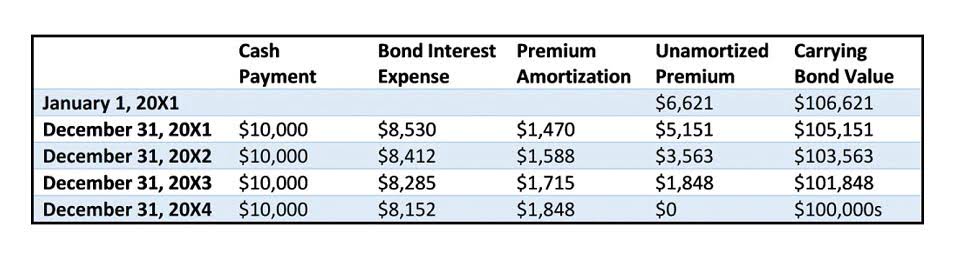
Examples of overtime calculations
It can only be awarded after an employee has worked 2 hours more than eight hours or more than the designated 40-hour workweek and is usually only awarded after 50 or more hours of work. It’s important for every employer to understand when and how to pay overtime rates. But the more important task is to reflect on why you are needing to pay overtime at all. While knowing how to calculate overtime compensation is important, no company wants to pay overtime more than they need to. Paying overtime depletes financial resources that could be better spent on improving the capacity of your team. A federal judge shut down the DOL’s latest overtime rule, reducing the total annual how much is overtime pay compensation requirement for exempt employees.

Calculate Overtime Pay for an Hourly Employee

Always check to ensure calculations comply with both federal and state law. Employees may be exempt from the FLSA and, thus, not entitled to overtime if they earn a salary that exceeds the FLSA minimum salary requirements and perform job duties that satisfy one of the established overtime-exempt roles. The most Interior Design Bookkeeping common exemptions include executive, administrative, professional, outside sales or computer-related jobs.
How To Calculate Overtime in 3 Steps
That said, employers are still mandated to pay overtime for their employees, especially after they worked after the mandated 8 hours a day/40 hour a week. The FLSA classes some employees as exempt from overtime pay rules, depending on the employee’s pay, whether they are paid on a salary or fee basis, and the duties they perform. Most exempt employees are in senior or executive roles, with higher salaries and more managerial duties.
- In the case of an audit, an employer must be able to prove payment of overtime that meets FLSA requirements.
- HR professionals also need to ensure that required wage/hour notices are posted.
- From the example above, the base pay was $800 and the overtime pay was $375.
- Finally, rework, or correcting mistakes in previously completed work counts as worked hours.
- For further guidance on FLSA requirements and overtime calculations, visit the U.S.
- Yes, part-time employees can be eligible for overtime pay if they work more than the legally defined standard work hours.
For example, for these states, if an employee works ten hours on Monday, six hours on Tuesday, and eight hours on Wednesday, Thursday, and Friday, you will not owe them overtime pay. This is different from some states above, which may require overtime pay for the two extra hours worked in a 10-hour day. The overtime premium cost equals the product of overtimehours, hourly cost rate, and labor cost multiplier. However, employers within the state are allowed to offer double time pay on their union contracts to entice employees to apply to their company.
Salaried Nonexempt Employees
Inquiries regarding representation will be subject to our potential-client intake and conflict check process. Delay may result in the waiver of claims or defenses, or otherwise harm you position. Therefore, we encourage you to continue your search for counsel while you await our response. The increase means that an exempt employee who is paid $844 a week (the equivalent of $43,888 a year) or more would not be subject to overtime.
Business
Shift differential pay is included in the weighted calculation of the regular pay rate for the purposes of determining overtime pay. Shift differential pay is not required by the federal government, unlike overtime pay, which is regulated by the FLSA, union contracts and state laws. What you may not know is many employers under-calculate wages that should be included in overtime payments or neglect to track hours for qualifying employees, subjecting them to lawsuits and penalties.